How to compute and display scalp potentials from EEG recordings
Created on July 7 at 12:34 pm - by: admin
EEG researchers commonly create spatial maps of the electrical activity acros the scalp. Data are interpolated or triangulated from a discrete number of electrode placements distributed across the scalp (generally greater than 32 sites) often in fixed/standardized positions (see, e.g., http://www.ant-neuro.com/products/waveguard_original).
To do this, electrode coordinates, either as {x, y, z} triplets or in spherical coordinates are needed and can be obtained from the manufacturer of electrode caps (e.g., https://www.egi.com/knowledge-center/item/71-sensor-position-files-for-visualizing-data-in-third-party-software).
Theoretical analysis typically involves modeling the head as a perfect sphere. The mapping of the electrode coordinates to the surface of a sphere can be accomplished with the following function:
Function scaleToSpherical(inWave) Wave inWave // offset the coordinates to the origin: MatrixOP/o/free wave0c=subtractMean(inWave,1) // compute the distance of electrodes from the origin: MatrixOP/O/free rawRad=sqrt(magsqr(col(wave0c,0))+magsqr(col(wave0c,1))+magsqr(col(wave0c,2))) // rescale the distance to a radius of 1: MatrixOP/O centeredNormalized=scalerows(wave0c,rec(rawRad)) End
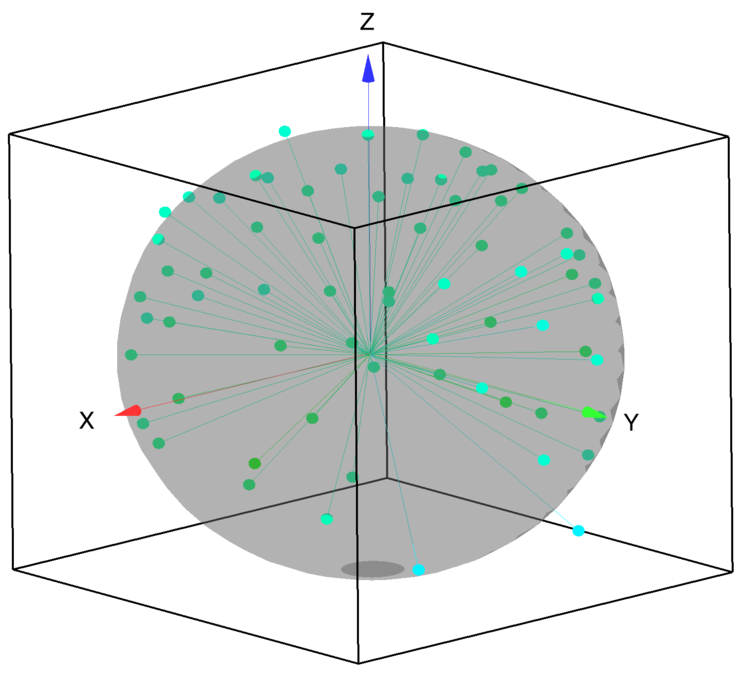
Figure 1:Initial electrode positions relative to the surface of a sphere.
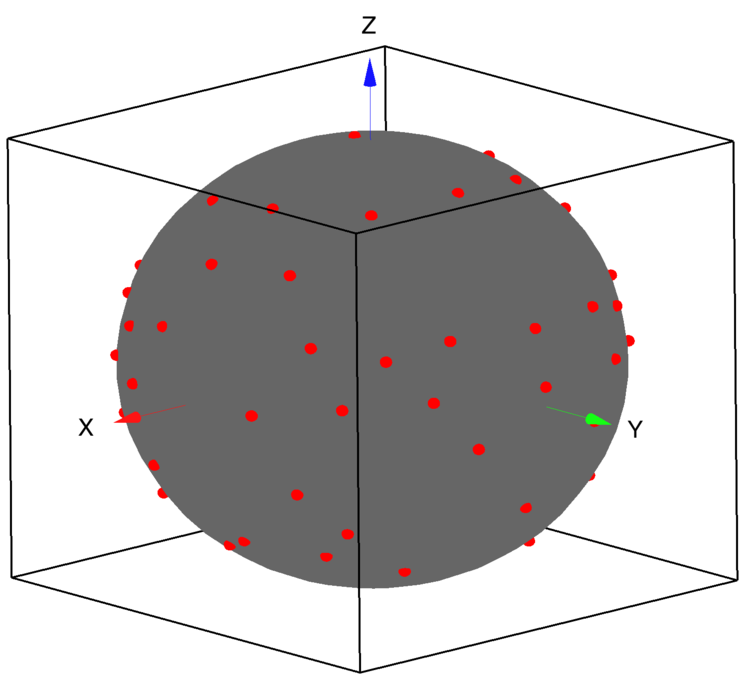
Figure 2: Normalized electrode coordinates on the surface of a sphere.
Using the normalized set of coordinates we can triangulate the data on the surface of a sphere using the SphericalTriangulate operation.
SphericalTriangulate centeredNormalized // this creates M_TriangulationData
Following the triangulation we can use the wave M_TriangulationData combined with the EEG data to interpolate the potentials at any point on the sphere. In order to display the resulting interpolation in Gizmo we start by creating a parametric surface representing the sphere.
Function makeParametricSphere(pointsx,pointsy) Variable pointsx,pointsy Variable i,j,rad Make/O/N=(pointsx,pointsy,3) parametricW Variable anglePhi,angleTheta Variable dPhi,dTheta dPhi=2*pi/(pointsx-1) dTheta=pi/(pointsy-1) Variable xx,yy,zz Variable sig for(j=0;j<pointsy;j+=1) angleTheta=j*dTheta zz=sin(angleTheta) if(angleTheta>pi/2) sig=-1 else sig=1 endif for(i=0;i<pointsx;i+=1) anglePhi=i*dPhi xx=zz*cos(anglePhi) yy=zz*sin(anglePhi) parametricW[i][j][0]=xx parametricW[i][j][1]=yy parametricW[i][j][2]=sig*sqrt(1-xx*xx-yy*yy) endfor endfor End
To complete the interpolation we need to construct one more wave: dataPointsWave. This wave has 4-columns consisting of the electrode coordinates in the first three columns and the potentials measured by each electrode at some fixed time t0 in the fourth column:
Variable nRows=DimSize(centeredNormalized,0) Make/O/D/N=(nRows,4) dataPointsWave dataPointsWave[][0,2]=centeredNormalized dataPointsWave[][3]=electrodePotentials[p]
The interpolation is computed by:
SphericalInterpolate M_TriangulationData,dataPointsWave,sphereData
The resulting interpolation is stored in the wave W_SphericalInterpolation where each row contains the scalar potential interpolated for the corresponding XYZ location in the wave sphereData. To display these values on the parametric surface we need to construct a color wave
Function createParametricColorWave(pWave,interpWave,reverseCTAB) Wave pWave,interpWave Variable reverseCTAB // set to 1 to reverse; 0 otherwise // the color wave must match the parametric surface: Variable rows=dimsize(pwave,0) Variable cols=dimSize(pWave,1) // Create the parametric color wave: Make/O/N=(rows,cols,4) pWaveColor=1 // find the range of values for scaling: Variable mmax=WaveMax(interpWave) Variable mmin=WaveMin(interpWave) // optionally replace the colortable here: ColorTab2Wave rainbow256 Wave M_Colors // not all colortables have the same number of colors: Variable nTableCols=DimSize(M_Colors,0)-1 if(reverseCTAB) MatrixOP/o/free aa=col(M_Colors,0) WaveTransform/o flip aa MatrixOP/O M_Colors=setCol(M_Colors,0,aa) MatrixOP/o/free aa=col(M_Colors,1) WaveTransform/o flip aa MatrixOP/O M_Colors=setCol(M_Colors,1,aa) MatrixOP/o/free aa=col(M_Colors,2) WaveTransform/o flip aa MatrixOP/O M_Colors=setCol(M_Colors,2,aa) endif MatrixOP/O M_Colors=fp32(M_Colors/65535) Variable nor=nTableCols/(mmax-mmin) Variable i, np=rows*cols,index,rr,cc for(i=0;i<np;i+=1) index=trunc((interpWave[i]-mmin)*nor) rr=mod(i,rows) cc=trunc(i/rows) pWaveColor[rr][cc][0]=M_Colors[index][0] pWaveColor[rr][cc][1]=M_Colors[index][1] pWaveColor[rr][cc][2]=M_Colors[index][2] endfor End
An example of this approach is illustrated in a cross-lingustic speech discrimination study at the following webpage:
Valerie L. Shafer, Ph.D.
vshafer@gc.cuny.edu
Professor and Deputy Executive Officer
Ph.D. Program in Speech-Language-Hearing Sciences
The Graduate Center, CUNY
365 Fifth Avenue, NY, NY 10016

Forum

Support
Gallery
Igor Pro 10
Learn More
Igor XOP Toolkit
Learn More
Igor NIDAQ Tools MX
Learn More





